Mastering Pool Chemistry: The Ultimate 2026 Guide to Perfect Water Balance
Have you ever pulled off the pool cover only to find a cloudy, green mess staring back at you? Or perhaps you’ve spent a fortune on chemicals, yet the water still irritates your eyes and smells like a chemistry lab. Maintaining a swimming pool can feel like a full-time job, but it doesn’t have to be a guessing game. In 2025, the intersection of public health standards and digital technology has made it easier than ever to achieve crystal-clear water.
Whether you are a new homeowner or a seasoned pro, understanding the “why” behind your water tests is the secret to a stress-free swim season. Let’s dive into the essential pillars of pool maintenance and how you can simplify the process using modern digital tools.
The Regulatory Framework: Evolution of the Model Aquatic Health Code and Industry Standards
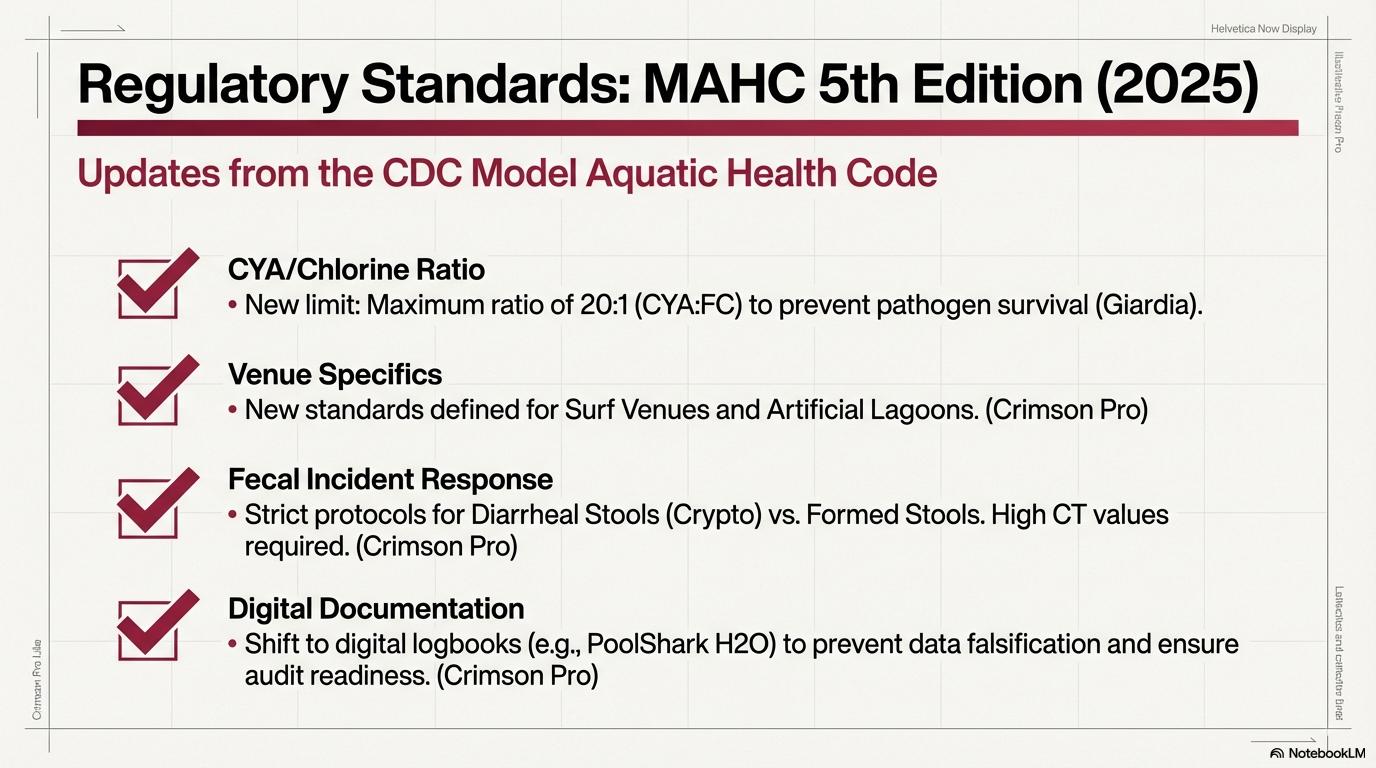
Aquatic safety in the United States isn’t just about clear water; it’s about public health. The foundational guidelines are set by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) through the Model Aquatic Health Code (MAHC). The most recent updates, including the 5th Edition released in late 2024, emphasize a scientific approach to preventing recreational water illnesses and injuries.
For the average pool owner, this means that “good enough” is no longer the standard. These regulations guide the manufacturing of the chemicals you buy and the testing protocols used by professionals. Following these standards ensures that your sanitizer is actually working to kill bacteria and that your water is safe for your family’s skin and eyes.
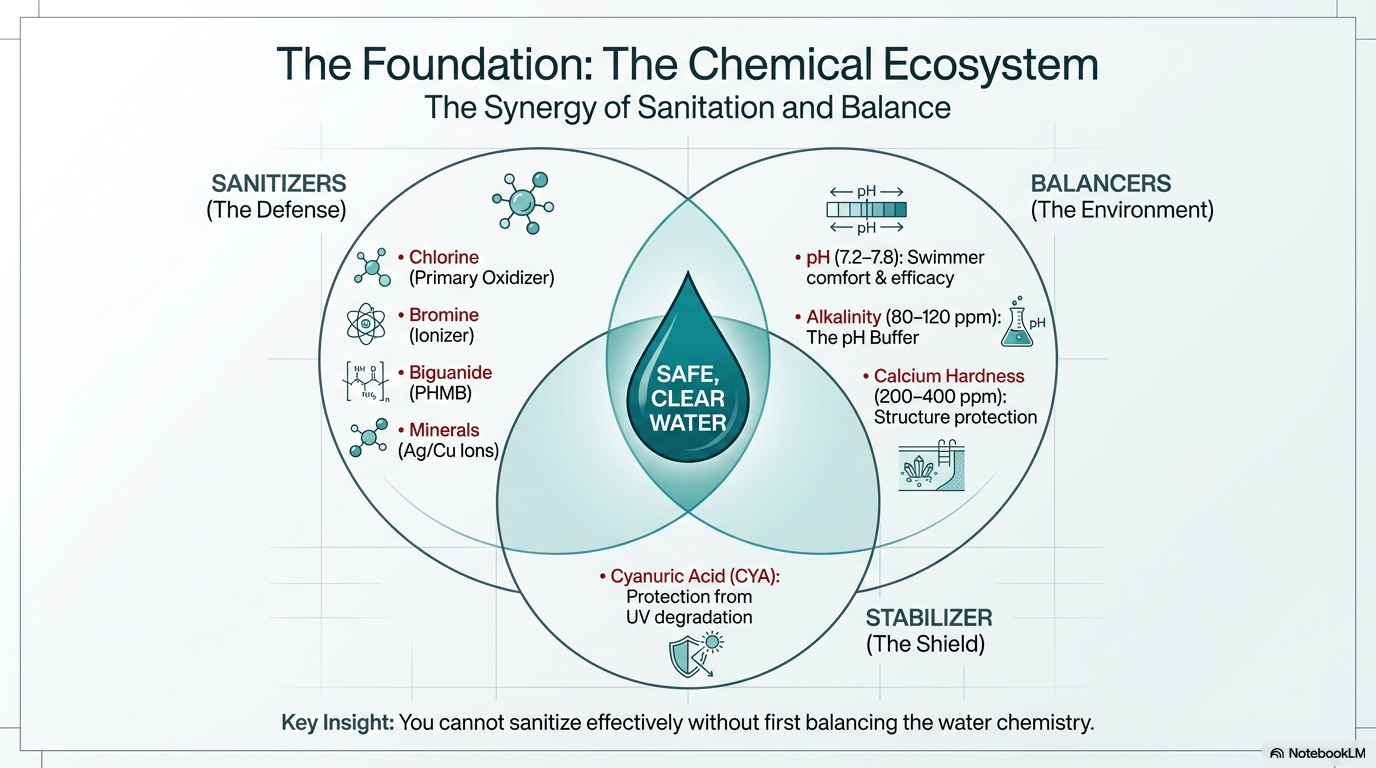
The Three Pillars of Pool Water Chemistry: Sanitization, pH, and Total Alkalinity

To keep your water healthy, you must manage three core components. Think of these as a tripod; if one leg is off, the whole thing falls over.
-
Sanitization (Chlorine): Chlorine is your primary defense against algae and bacteria. You need to maintain a “Free Chlorine” level that is high enough to kill germs but low enough to be safe for swimmers. Remember, “Total Chlorine” isn’t the same as “Free Chlorine”—total includes “Combined Chlorine,” which is the “used up” chlorine that causes that strong chemical smell and eye irritation.
-
pH Balance: This measures how acidic or basic your water is. Your goal is a pH of 7.4 to 7.6, which is the same as the human eye. If the pH is too high, your chlorine becomes less effective; if it’s too low, the water becomes “aggressive” and can corrode your pool equipment.
-
Total Alkalinity (TA): Alkalinity acts as a buffer for your pH. It prevents “pH bounce,” where your levels swing wildly after a rainstorm or heavy use. Keeping TA in the 80–120 ppm range ensures your pH stays stable.
Advanced Metrics: Understanding LSI, CYA, and Calcium Hardness
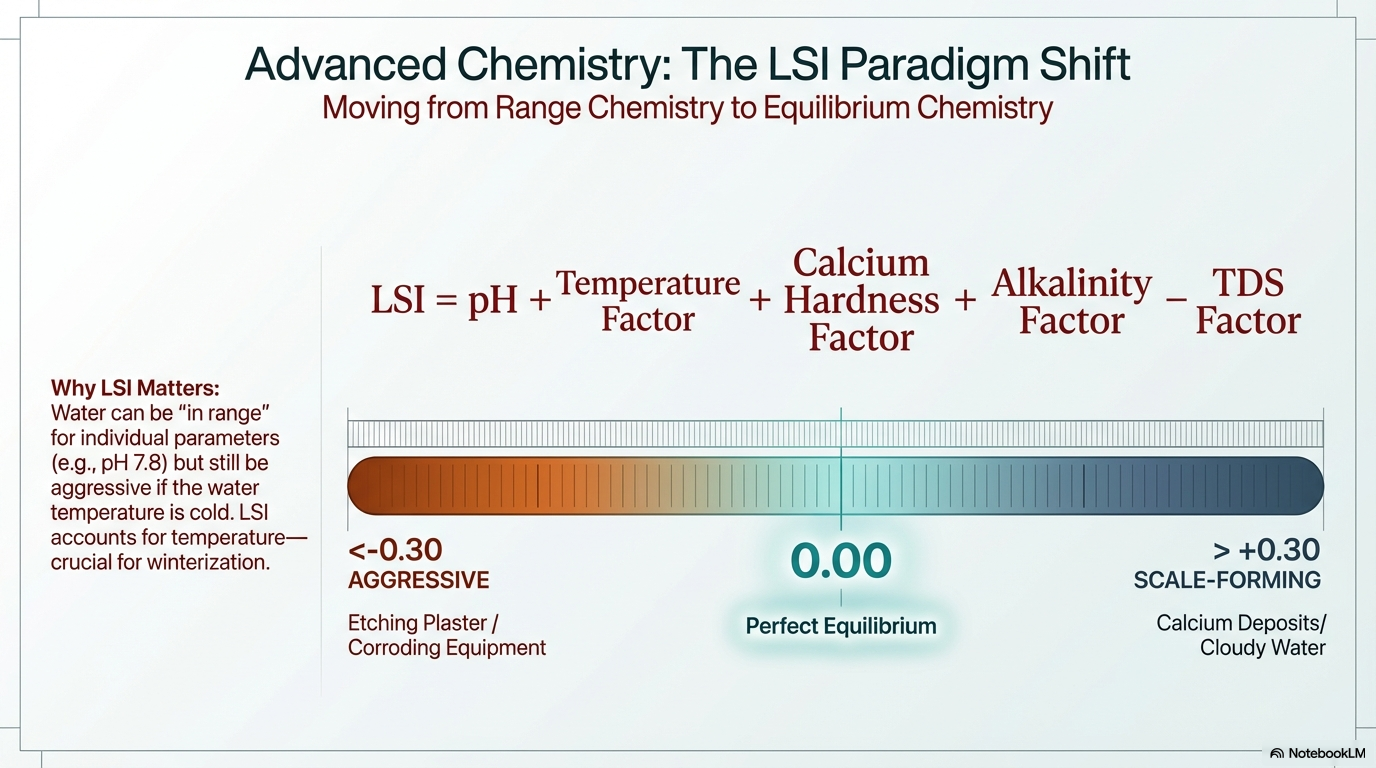
Once you master the basics, you need to look at the factors that protect your pool’s physical structure.
-
Cyanuric Acid (CYA): Also known as “stabilizer,” this acts as sunscreen for your chlorine. Without it, the sun can burn off your chlorine in hours. However, too much CYA (over 50 ppm) leads to “over-stabilization,” making your chlorine effectively useless.
-
Calcium Hardness: This measures the amount of dissolved calcium in the water. If it’s too low, the water becomes “hungry” and will leach calcium out of your pool’s plaster or grout, causing permanent damage.
-
The Langelier Saturation Index (LSI): This is the ultimate “balance” score. It uses an equation involving pH, temperature, and calcium to tell you if your water is aggressive (leaching) or scale-forming (leaving crusty white deposits).
Digital Transformation: The Rise of Smart Testing and Automated Monitoring
Gone are the days of trying to match a tiny strip of paper to a color chart while squinting in the sun. The market for pool water quality testing is shifting toward digital solutions, with a projected value of $615 million by 2031.
Digital test kits and apps, like the Pool Chemical Calculator, remove the human error associated with visual color comparison. For commercial operators, tools like the LaMotte WaterLink SpinTouch provide professional-grade accuracy in under 60 seconds. For homeowners, having a digital “source of truth” means you stop over-treating your pool and start saving money on chemicals.
Common Testing Mistakes and How to Avoid Them

Even with the best kit, small errors can lead to big problems. Avoid these “water test fails”:
-
Sampling from the surface: Always take your water sample from at least 12 inches deep, away from return jets, to get a representative mix of the water.
-
Using expired reagents: Liquid reagents typically last about a year; if they are stored in the sun or heat, they expire even faster.
-
Improper storage: Chemicals and test kits should be kept in a cool, dry place to maintain their chemical integrity.
Economic Drivers and Market Trends in the Water Quality Sector
The pool industry is a significant part of the $563.7 billion outdoor recreation economy. Because of this, we are seeing a massive push toward efficiency. Pool owners are looking for ways to reduce the “cost of ownership,” which has led to a surge in demand for saltwater systems and variable-speed pumps. By using a digital calculator to maintain precise levels, you can extend the life of these expensive components, preventing premature scale buildup or corrosion.
Conclusion: Making Waves with Data-Driven Pool Care
Maintaining a pool shouldn’t feel like a science experiment gone wrong. By focusing on the “Four Pillars” of proactive care—balancing your water, managing your LSI, and using accurate digital tools—you can spend less time testing and more time swimming.
Modern pool care is about being proactive rather than reactive. Instead of waiting for the water to turn green, use the data at your fingertips to keep it perfect year-round.
Ready to stop the guesswork? Take the “math” out of pool maintenance today. Download the Pool Chemical Calculator for precise dosing, easy-to-follow instructions, and a crystal-clear pool all season long. Download on the Google Play Store
Internal Links to Explore:
Recommended Products
As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases.
- Taylor K-2006 Complete Pool Water Test Kit ($90) — The gold standard of pool test kits. Tests for free/combined chlorine, pH, alkalinity, calcium hardness, and CYA with professional-grade accuracy.
- In The Swim 3-Inch Chlorine Tablets (25 lbs) ($70) — Stabilized trichlor tablets for consistent, slow-dissolving chlorination. 25-lb bucket lasts most pools an entire season. Use in a floating dispenser or chlorinator.
- Clorox Pool&Spa pH Down (5 lbs) ($13) — Sodium bisulfate granules for safely lowering pool pH. Easy-to-use and dissolves quickly.
- Arm & Hammer Baking Soda (15 lbs) ($15) — Pure sodium bicarbonate — the same product pool stores sell as ‘alkalinity increaser’ at 3x the price. Raises alkalinity without significantly affecting pH.
- Dolphin Nautilus CC Plus Robotic Pool Cleaner ($800) — Our #1 pick for hands-free pool cleaning. Cleans floors, walls, and waterline in 2 hours. Built-in filtration — no hoses, no booster pump needed.
- In The Swim Cal-Hypo Pool Shock (24 x 1 lb bags) ($62) — 68% calcium hypochlorite shock in individually wrapped 1-lb bags for precise dosing. One bag per 10,000 gallons for routine weekly shocking.





