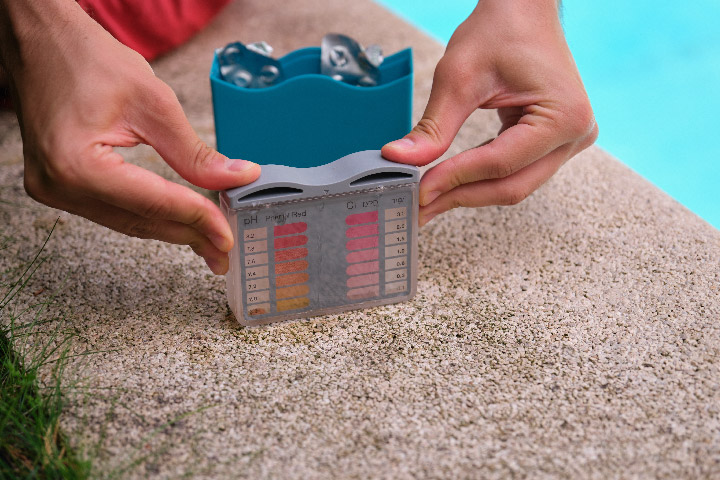
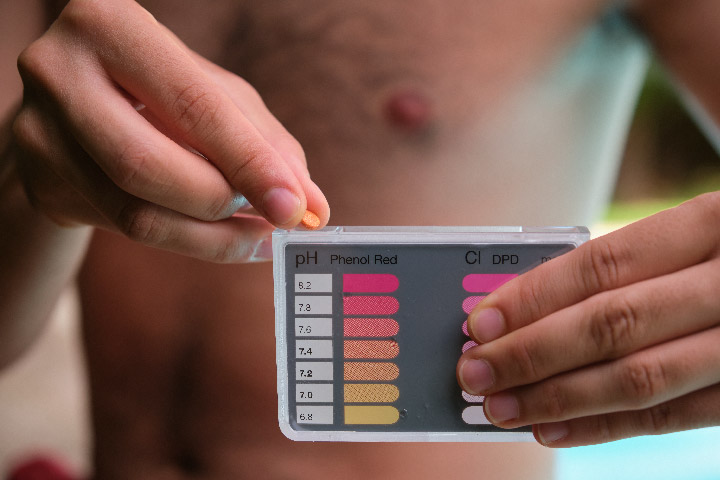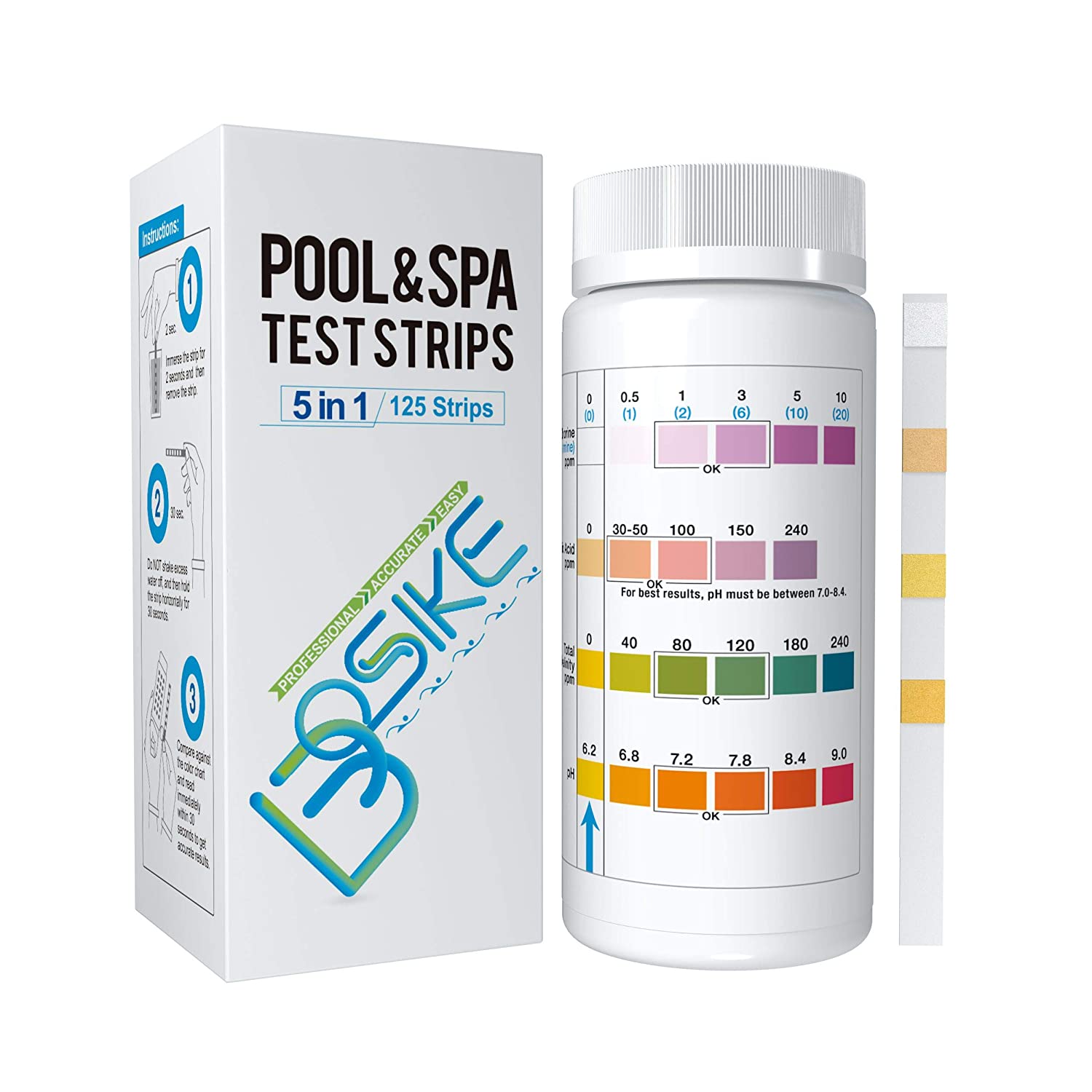
How to Lower pH in a Swimming Pool: A Comprehensive Guide for Pool Owners
Achieve the Ideal pH Balance for a Healthy and Comfortable Swimming Experience Introduction Maintaining the correct pH level in your swimming pool is essential for ensuring a comfortable swimming experience,
The Saltron Mini Chlorine Generator: Revolutionizing Spa Sanitation and the Benefits of a Salt Water Spa
Keeping your spa clean and safe for users is essential, but traditional sanitation methods can be cumbersome, costly, and may involve harsh chemicals. The Saltron Mini Chlorine Generator, specifically designed
Pool Safety Covers: A Must-Have Accessory for New Pool Owners
Understanding the Importance, Types, and Benefits of Pool Safety Covers As a new pool owner, ensuring the safety of your family and guests should be a top priority. One of
Identifying and Removing Pool Stains: A Comprehensive Guide
Keep Your Pool Surface Sparkling Clean with Effective Stain Identification and Removal Techniques Introduction Pool stains can be an eyesore and may affect the overall aesthetics of your swimming pool.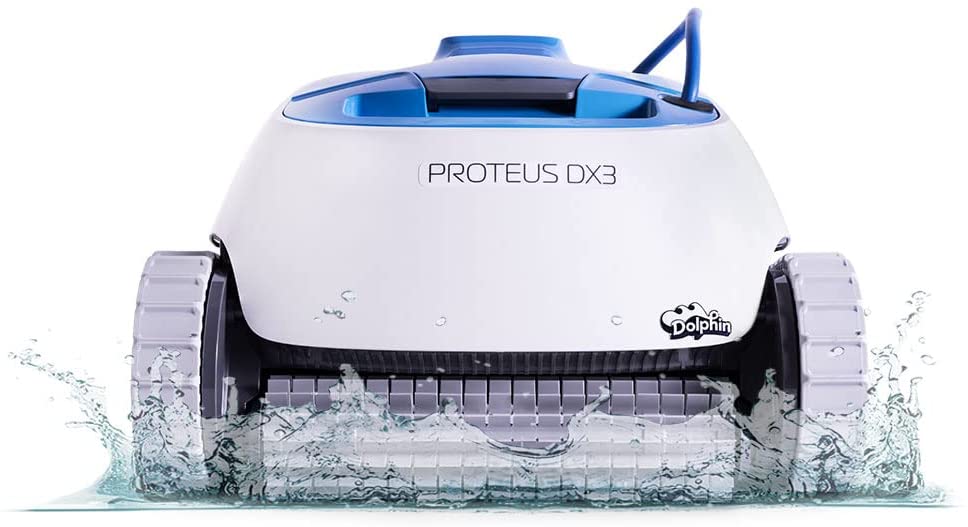
Troubleshooting Robotic Pool Cleaners: A Comprehensive Guide to Diagnosing and Fixing Common Issues
Keep Your Pool Immaculate with a Properly Functioning Robotic Pool Cleaner Introduction Robotic pool cleaners are an efficient and convenient way to keep your swimming pool clean and free of
Demystifying Pool Flocculant: Understanding Its Purpose, Benefits, and Drawbacks
A Comprehensive Guide to Pool Flocculant, Its Applications, and Factors to Consider Before Using It Introduction Pool flocculant is a chemical treatment that plays a vital role in maintaining crystal-clear
Conquering Black Algae in Your Home Swimming Pool: Causes, Solutions, and Products
Learn How to Identify, Eliminate, and Prevent the Stubborn Invader That Is Black Algae Introduction Black algae can be a persistent and challenging issue for many homeowners with swimming pools.
Choosing the Perfect Fence for Your Above Ground Pool: A Comprehensive Guide
Enhancing Safety, Aesthetics, and Functionality with the Right Above Ground Pool Fence Introduction A fence around your above ground pool serves several essential functions, such as providing privacy, enhancing safety,