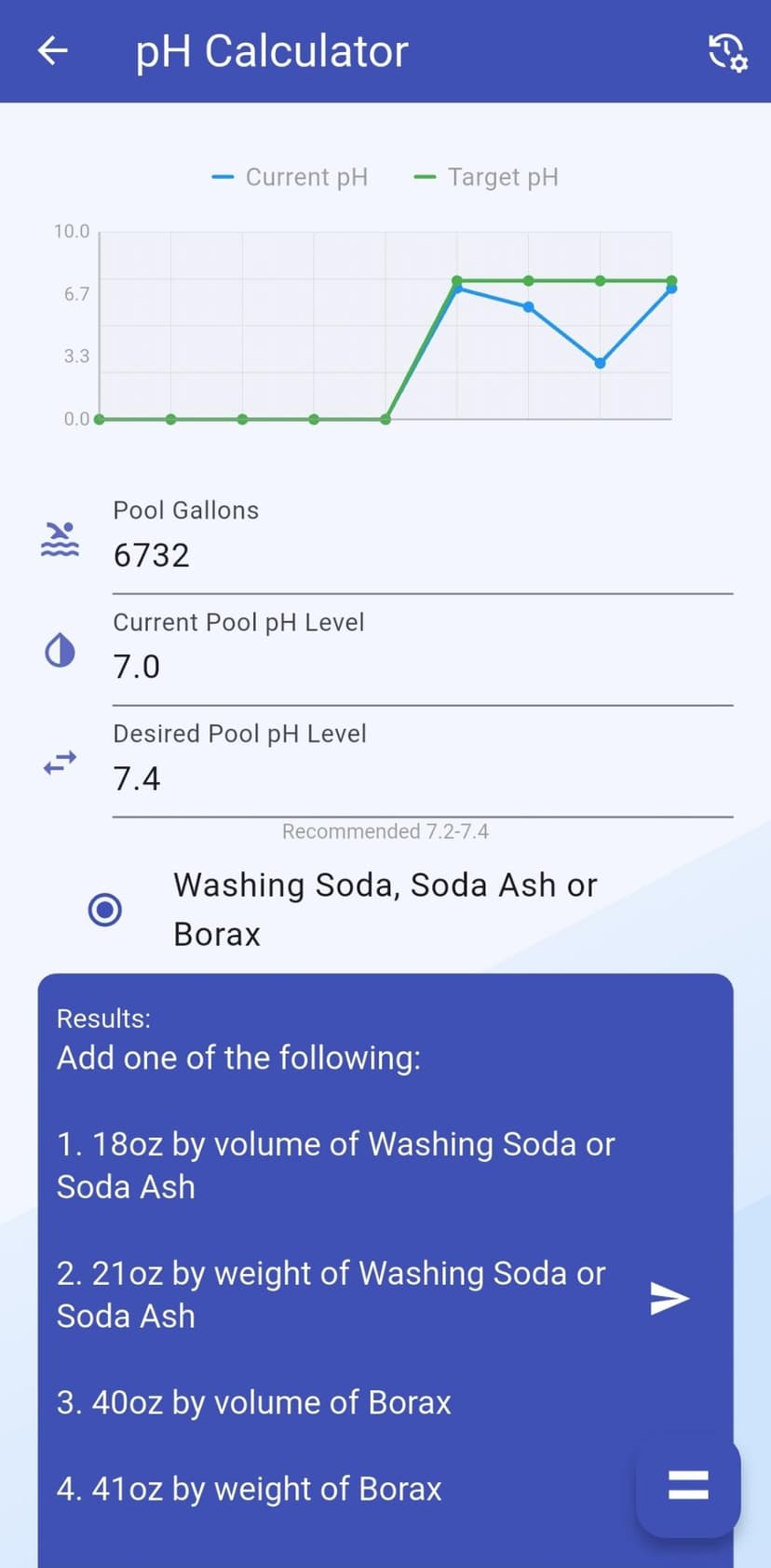
pH Calculator
Maintain proper pH (7.4 - 7.6) for swimmer comfort and sanitizer efficiency.
*Accurate pH adjustments require knowing your Alkalinity.
pH is good!

pH Up
Raise pool pH effectively.

pH Down
Lower pool pH effectively (Dry Acid).
Low pH Effects (< 7.2)
When pH drops below 7.2, water becomes acidic and aggressive. It actively seeks minerals to satisfy its hunger, stripping them from your pool surfaces. This leads to etched plaster, brittle vinyl liners, corroded metal heater cores, and stinging eyes for swimmers. It essentially eats away at your investment.
High pH Effects (> 7.8)
As pH climbs above 7.8, water becomes scale-forming. Dissolved calcium begins to fall out of solution, creating rough scale on surfaces and turning the water cloudy. High pH also severely reduces chlorine's cleaning power—at pH 8.0, your chlorine is less than 10% effective against bacteria.
How to Raise pH
To raise pH, use Sodium Carbonate (Soda Ash) for large adjustments or Sodium Borate (Borax) for smaller tweaks. Aerating the water—turning on fountains, waterfalls, or pointing return jets upward—will also naturally raise pH over time by off-gassing carbon dioxide.

pH Up
Raise pool pH effectively.
How to Lower pH
To lower pH, use Muriatic Acid (liquid) or Sodium Bisulfate (dry acid). Muriatic acid is generally cheaper and more effective but requires careful handling. Always add acid to water (never water to acid) and pour it slowly near a return jet to ensure rapid mixing.

pH Down
Lower pool pH effectively (Dry Acid).
| pH Level | Effective Free Chlorine |
|---|---|
| 6.0 | 97% |
| 7.0 | 75% |
| 7.2 | 63% |
| 7.5 (Ideal) | 49% |
| 7.6 | 39% |
| 7.8 | 28% |
| 8.0 | 3% |
Go Pro with Mobile
Track pH history, manage multiple pools, and get precise dosing recommendations on the go.